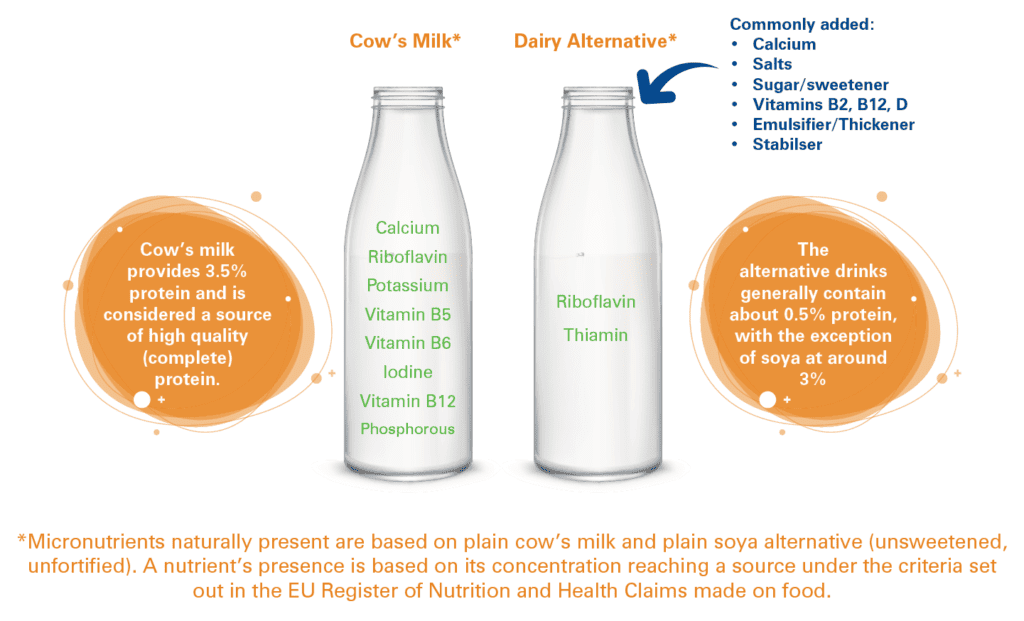
While they are sometimes used as a replacement for cow’s milk, they are not nutritionally equivalent.
The main difference is that dairy alternative drinks are often fortified with nutrients such as calcium and vitamin B12, while dairy milk is a natural source of a much wider matrix of other nutrients (including protein, vitamin B2, vitamin B5, iodine, potassium and phosphorus). The form of calcium in many fortified drinks is different to that naturally provided by dairy so it is uncertain whether its absorption and metabolism in the body is exactly the same. Separation of ingredients may occur in some dairy alternative drinks, causing a calcium residue to settle at the bottom of the carton. Therefore, such drinks should be well shaken.
Other differences between cow’s milk and dairy alternative drinks include price, number of ingredients, country of origin and air miles.